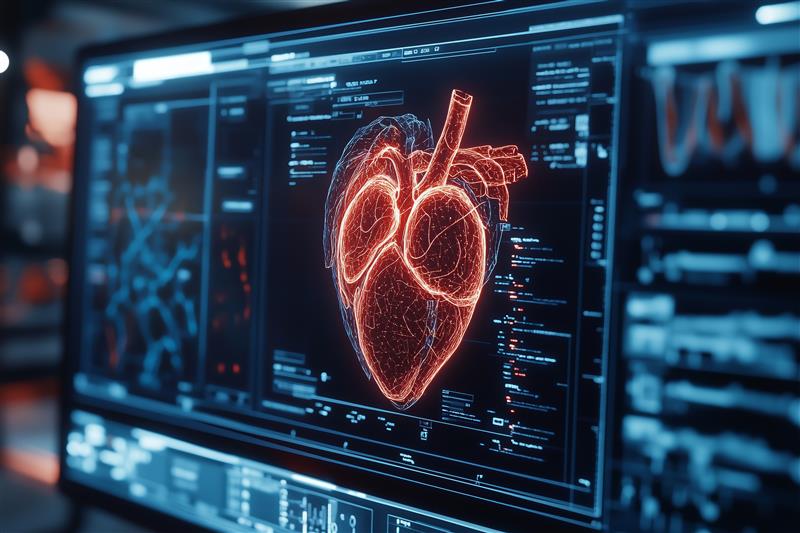
Heart disease is the leading cause of death worldwide, but the good news is that many forms are preventable with the right knowledge and lifestyle choices. Often referred to as a “silent killer,” heart disease can progress quietly for years before symptoms become apparent.
In this article, we’ll break down what heart disease is, explore its root causes, identify common warning signs, and offer practical, doctor-approved prevention tips to help you protect your heart and live a longer, healthier life.
❤️ What Is Heart Disease?
Heart disease is a broad term for a range of conditions that affect the heart and blood vessels. The most common type is coronary artery disease (CAD), which reduces blood flow to the heart.
Types of Heart Disease Include:
- Coronary artery disease (CAD)
- Heart failure
- Arrhythmias (irregular heartbeat)
- Heart valve disease
- Congenital heart defects (present at birth)
- Cardiomyopathy (weakened heart muscle)
These conditions can lead to serious complications such as heart attack, stroke, or sudden cardiac death.
🔍 Common Causes and Risk Factors
Heart disease doesn’t have just one cause—it usually results from a combination of genetic, lifestyle, and environmental factors.
Major Risk Factors:
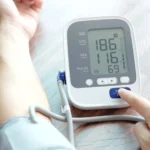
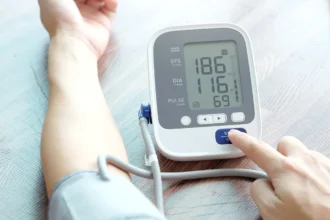
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- High cholesterol
- Smoking
- Diabetes or prediabetes
- Obesity
- Physical inactivity
- Unhealthy diet
- Excessive alcohol use
- Chronic stress
- Family history of heart disease
Tip: Many of these factors are modifiable through healthy lifestyle changes.
⚠️ Early Warning Signs to Watch For
Heart disease can be “silent,” but some symptoms may signal trouble. If you notice any of the following, don’t ignore them—early detection can save your life.
Common Symptoms:
- Chest pain or discomfort (especially during activity)
- Shortness of breath
- Pain in the neck, jaw, arms, or back
- Fatigue or weakness
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Swelling in the legs, ankles, or feet
- Irregular heartbeat or palpitations
- Nausea or cold sweats
Note: Symptoms may differ between men and women. For example, women may experience more fatigue, nausea, or jaw pain during a heart attack.
🛡️ Heart Disease Prevention Tips
The good news is that up to 80% of cardiovascular diseases are preventable through simple, consistent habits.
🥗 1. Eat a Heart-Healthy Diet
- Prioritize fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes
- Choose lean proteins (fish, poultry, beans)
- Limit saturated fats, trans fats, and added sugars
- Reduce sodium intake to manage blood pressure
- Try the DASH or Mediterranean diet for optimal results
🏃♂️ 2. Stay Physically Active
- Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous activity per week
- Walking, swimming, cycling, and strength training all support heart health
🚭 3. Quit Smoking and Limit Alcohol
- Smoking is a leading cause of heart disease. Quitting can cut your risk in half within a year
- Keep alcohol intake moderate (1 drink/day for women, 2 for men)
⚖️ 4. Maintain a Healthy Weight
- Excess weight strains your heart and raises your risk for diabetes and hypertension
- Focus on gradual, sustainable weight loss if needed
🧘 5. Manage Stress Effectively
- Chronic stress can increase blood pressure and inflammation
- Try meditation, deep breathing, yoga, journaling, or counseling
🩺 6. Get Regular Health Screenings
- Monitor blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar regularly
- Catching problems early leads to more effective treatment and fewer complications
🧠 Did You Know?
- A heart attack can occur without chest pain—especially in women, seniors, and diabetics.
- Laughing, spending time with loved ones, and maintaining positive relationships can lower heart disease risk.
- Sleep deprivation increases the risk of heart problems by affecting blood pressure and inflammation levels.
🙋 8 Unique FAQs About Heart Disease
Q1: Can you reverse heart disease?
A: While you can’t undo all damage, healthy lifestyle changes can slow or even partially reverse plaque buildup in arteries.
Q2: Is heart disease only a concern for older people?
A: No—risk can begin in your 20s or 30s, especially with poor diet, smoking, or sedentary habits.
Q3: Are genetics a death sentence for heart disease?
A: Genetics increase risk, but lifestyle choices greatly influence whether you develop heart problems.
Q4: Can stress alone cause a heart attack?
A: Chronic stress contributes to high blood pressure and inflammation, which are heart disease risk factors. Severe stress can even trigger stress cardiomyopathy, also known as “broken heart syndrome.”
Q5: What’s the difference between a heart attack and cardiac arrest?
A: A heart attack is a circulation issue (blocked artery), while cardiac arrest is an electrical issue (heart stops beating). Both are medical emergencies.
Q6: Is cholesterol always bad for your heart?
A: Not all cholesterol is harmful. HDL (good) cholesterol helps protect your heart, while LDL (bad) cholesterol increases risk.
Q7: How does diabetes increase heart disease risk?
A: High blood sugar can damage blood vessels and nerves that control the heart, raising the risk for cardiovascular complications.
Q8: How often should I get my heart checked?
A: Adults should get regular screenings every 1–2 years—or more often if you have risk factors.
💡 Conclusion: Take Your Heart Health to Heart
Heart disease is serious—but it’s also largely preventable. By understanding the causes and recognizing the warning signs early, you can take powerful steps to protect your heart. Through consistent lifestyle choices, regular screenings, and professional guidance, you’re investing in a longer, healthier, and more energetic life.
Your heart works hard for you every day—start working hard for your heart today.