High blood pressure—also known as hypertension—is often called the “silent killer” for a reason. It usually has no obvious symptoms but can lead to serious health complications like heart disease, stroke, and kidney damage if left unmanaged. That’s why monitoring your blood pressure (BP) is one of the most crucial steps in protecting your long-term heart health.
In this article, we’ll explore how high blood pressure affects your heart, why regular monitoring is essential, and what you can do to maintain a healthy BP.
What Is Blood Pressure?
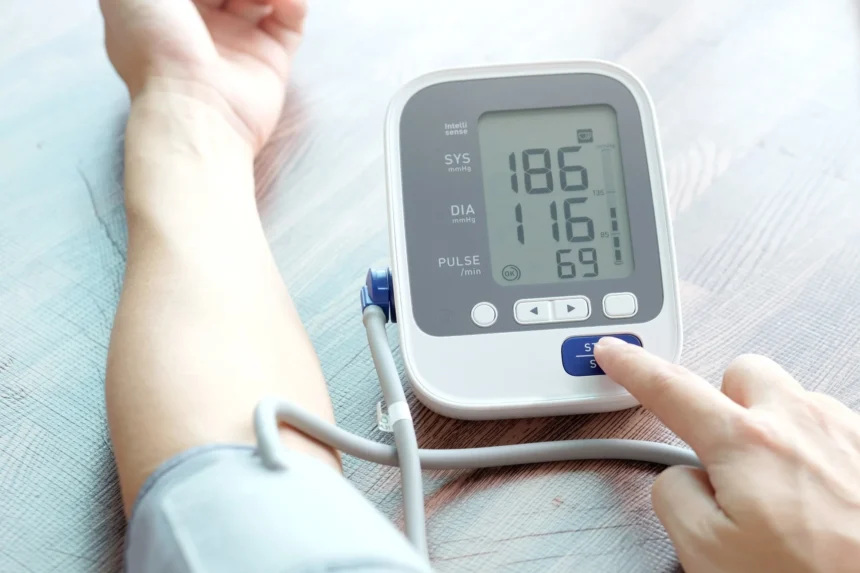
Blood pressure is the force of blood pushing against your artery walls as your heart pumps. It’s recorded as two numbers:
- Systolic pressure (top number): The pressure when your heart beats
- Diastolic pressure (bottom number): The pressure when your heart rests between beats
Normal BP: Less than 120/80 mm Hg
Elevated BP: 120–129/<80 mm Hg
Stage 1 Hypertension: 130–139/80–89 mm Hg
Stage 2 Hypertension: 140+/90+ mm Hg
How High Blood Pressure Affects the Heart
Chronic high blood pressure forces your heart to work harder than normal. Over time, this extra effort can cause several serious conditions:
❤️ 1. Heart Attack
High BP can lead to narrowed arteries, restricting blood flow to the heart and increasing the risk of blockages.
💓 2. Heart Failure
The heart muscle can enlarge or weaken, reducing its ability to pump efficiently and causing fluid buildup in the lungs or legs.
🧠 3. Stroke
Hypertension is a major risk factor for both ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes, caused by blocked or burst blood vessels in the brain.
🔁 4. Irregular Heartbeat (Arrhythmia)
High BP may contribute to atrial fibrillation, increasing your stroke risk.
🩺 5. Aneurysms
Constant pressure can weaken artery walls, forming bulges that may rupture—a life-threatening event.
Why Monitoring Your Blood Pressure Matters
🩹 Early Detection Saves Lives
Because high BP often has no symptoms, regular monitoring can detect problems before they lead to serious complications.
📉 Track Treatment Effectiveness
If you’re on medication or following a lifestyle change, tracking your BP helps determine what’s working—and what’s not.
👨⚕️ Personalized Care
Blood pressure readings give your doctor vital information to tailor your care and adjust treatment plans as needed.
🧘♀️ Increased Awareness = Better Habits
Seeing your BP numbers can motivate you to eat healthier, exercise more, and avoid risky behaviors like smoking or excessive drinking.
How to Monitor Your Blood Pressure at Home
Home blood pressure monitors are affordable, easy to use, and help you stay proactive.
📋 Tips for Accurate Readings:
- Sit calmly for 5 minutes before measuring
- Keep your arm at heart level
- Avoid caffeine, exercise, or smoking 30 minutes beforehand
- Use a validated digital monitor with an upper-arm cuff
- Take readings at the same time each day
Pro Tip: Record your readings in a journal or app to share with your healthcare provider.
What Causes High Blood Pressure?
Several factors can contribute to high BP, including:
- Poor diet (high in sodium, low in potassium)
- Lack of physical activity
- Obesity or being overweight
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Smoking
- Chronic stress
- Genetic predisposition
- Medical conditions (e.g., kidney disease, diabetes)
Lifestyle Tips to Lower and Manage High BP
🥗 1. Eat a Heart-Healthy Diet
Follow the DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) plan:
- High in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
- Low in sodium, red meats, and added sugars
- Rich in potassium, magnesium, and fiber
🏃♂️ 2. Stay Active
Aim for 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming.
🧘♀️ 3. Reduce Stress
Practice relaxation techniques like:
- Deep breathing
- Meditation or mindfulness
- Yoga
- Journaling or nature walks
🚭 4. Quit Smoking and Limit Alcohol
Both can raise BP and damage your arteries.
⚖️ 5. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Losing even 5–10% of your body weight can make a significant difference in lowering BP.
💊 6. Take Medications as Prescribed
If lifestyle changes aren’t enough, your doctor may prescribe:
- Diuretics
- ACE inhibitors
- Beta-blockers
- Calcium channel blockers
Never skip or adjust medication without consulting your provider.
When to See a Doctor
Seek medical advice if you:
- Consistently record BP above 130/80 mm Hg
- Experience symptoms like chest pain, dizziness, or shortness of breath
- Have a family history of heart disease or stroke
- Are pregnant (pregnancy-induced hypertension can be dangerous)
Final Thoughts
High blood pressure doesn’t have to lead to heart disease—but ignoring it can be dangerous. By regularly monitoring your BP and making heart-healthy lifestyle choices, you take control of your future and significantly reduce your risk of serious complications.
Remember, knowledge is power. Knowing your numbers today can save your life tomorrow.
FAQs: Blood Pressure and Heart Health
1. How often should I check my blood pressure?
At least once a year if normal, more often if elevated or you’re on medication.
2. Can I feel when my BP is high?
Usually not. High BP often has no symptoms, which is why monitoring is key.
3. Does salt really affect blood pressure?
Yes. Reducing sodium intake can help lower BP, especially in salt-sensitive individuals.
4. Can stress cause high blood pressure?
Chronic stress may lead to sustained BP increases and unhealthy habits that contribute to hypertension.
5. What’s the best time to measure BP at home?
Morning before eating or taking medication and in the evening, unless otherwise advised by your doctor.
6. Is low blood pressure dangerous too?
It can be if it causes dizziness, fainting, or poor circulation—but is usually less risky than high BP.
7. Can young people have high blood pressure?
Yes. Lifestyle factors and genetics can affect BP at any age.
8. Will I need BP medication forever?
Not always. Some people can manage BP through lifestyle changes and reduce or stop medications under medical supervision.